There are several theories regarding the origin of the term chicken pox. It is often stated to be a modification of chickpeas (based on resemblance of the vesicles to chickpeas), or due to the rash resembling chicken pecks.
CHICKENPOX SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Initial symptoms:
- Fever, feeling ill, sore throat, body ache, headache and loss of appetite.
Particular Symptom:
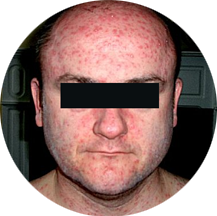
- The rash appears a day after initial symptoms begin. Skin rash mainly on the body and head rather than on the limbs.
- Rash starts as clusters of small, itchy, red blisters
- This blister bursts then dries up, crust, and form scabs.
- New clusters of blisters continue to appear for a few days.
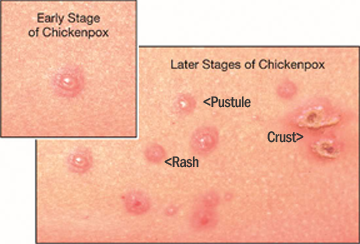
How long does chicken pox last?
- New blisters develop for four days.
- By sixth day complete crusting happens.
- Crust then take 7-14 days to fall off, and may leave marks on the skin that take time to fade.
How does chicken pox spread?
- Highly spreading disease.
- If you have not had chickenpox and have not been fully vaccinated against varicella, you can become infected by breathing in airborne traces of the virus or touching an area of chickenpox rash on an infected person.
- Chickenpox virus is in the rash & respiratory discharge therefore spreads easily through coughing or sneezing of ill individuals or through direct contact with secretions from the rash.
- A person with chickenpox is infectious one to two days before the rash appears.
- They remain contagious until all lesions have crusted over (this takes approximately six days).
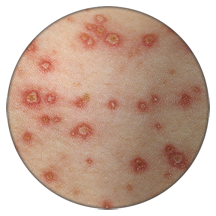
PREVENTING CHICKEN POX
Stay away:
- Sneeze spray, fluid from the nose, drops from the cough of chickenpox patient contains the Virus therefore stay away from these.
- Avoid using the personal belongings of the patient.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after coming home from public place.
- Don’t put your finger frequently into your nose-mouth.
- Cover your nose and mouth when the patient coughs or sneezes.
- Avoid rubbing against fellow passengers in crowded public transport.
Homeopathic preventive: Take single dose of Variolinum 200 empty stomach for three days.
Special precaution group:
- Pregnant women
- Newborn babies
- People whose immune systems may be compromised, including those with HIV, or who have received an organ or bone marrow transplant
Can you catch chickenpox twice? Most people who have had chickenpox earlier do not develop chickenpox a second time. However, there are rare cases in which a person can develop chickenpox a second time. In some people, the virus can resurge later in life, causing a related condition called shingles.
CHICKENPOX TREATMENT
Managing symptoms — Simple treatments can usually ease fever and itchiness caused by chickenpox.
Fever Treatment:
- Treat a mild fever with Bio-chemic Medication (Ferrum phosphoricum) if it is below 101.5 and your child/patient is feeling relatively OK.
- If medication is necessary because your child is bothered by the fever or the fever is above 102oC, along with cold sponging consult pediatrician and choose an anti-pyretic.
- Never use aspirin because of the risk of Reye’s syndrome
- Ibuprofen is also not recommended because it might increase the risk of severe streptococcal skin infections. Peptic ulcer.
Locally for the rash:
- You can apply Calendula cream.
- Cool/lukewarm baths in which you can add 2 ounces (60 ml) baking soda per tub.
- Calamine Lotion: apply lotion to the chickenpox that itch the most or massage them with an ice cube for 10 minutes.
Scratching the skin can cause a skin infection because bacteria hide beneath the fingernails. Scratching may also increase the chances of developing a scar. Fingernails should be clipped to reduce these risks.
HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENT:
Look for the below indications of most commonly used remedies in homeopathy to treat chickenpox. It is always better to consult your health provider before using
Antim tart:
- Rattling Cough,
- Pus filled rash,
- high fever and severe sweating with coldness & trembling, worse in the evening.
Antim crude:
- Rash fluid filled, pus filled, thick crust, burning itching worse at night,
- Do not want to be touched,
- Cold feeling even in warm room,
- Nausea vomiting & white coated tongue.
Aconite:
- Sudden violent onset of symptoms. All the symptoms are severe.
Belladona:
- First stage, high grade burning fever with no thirst,
- Short dry cough,
- Dry hot red skin, burning, sudden spreading of rash,
- Glands swollen painful.
Rhus tox:
- Exposure to air causes dry teasing cough from midnight until morning,
- Restless during fever, painful joints better by movements,
- Skin red swollen, intense itching, fluid filled eruptions with tendency to crust formation,
- Caused after overexertion.
Pulsatilla:
- Loss of appetite & thirst,
- Dry cough makes you sit up, thick greenish yellowish mucus, chest feels tight & painful,
- Skin troubles worse while changing dress, and rich oily food,
- During fever no thirst, external heat intolerable with blue distended veins,
- Wants to breath in open air, open space.
Variolinum:
- High fever, lot of bad smelling sweating,
- Skin dry hot, with pus filled eruption,
- Breathing difficult,
- Acts as a vaccine.
Mezerium:
- During the last stage of Crusting especially head, crust separation reveals honey like fluid underneath.
DIET CONSIDERATIONS:
- A diet rich in whole foods, with plenty of vegetables and fruits in a variety of colors. This “rainbow diet” has been shown to provide the phyto-nutrients needed to strengthen the immune system.
- Juices rich in vitamin A and C, such as fresh carrot juice or fresh squeezed lemon juice with water and honey.
- Chicken soup (chicken should be organic)
- Vegetable Soup
- Shakes/Smoothies with kale, cabbage, beet, broccoli
- For painful mouth and throat ulcers, a soft diet (avoid ) should be used.
- Limit sugar and salt.
CHICKENPOX COMPLICATIONS
Potential complications of chickenpox include:
- Skin infections
- Pneumonia, an infection of the lungs
- Encephalitis, inflammation of the brain

Very good….even common man can be benefitted by this information.
Thanks for yourbest information for all.